CORE TECHNOLOGY
iPS-Derived Exosomes
What Are iPS Exosomes?
iPS Exosomes are extracellular vesicles secreted by induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). These nano-sized particles (30-150nm) carry proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids that can influence cellular behavior.
iPSCs, which are expected to be used in regenerative medicine, are being researched worldwide. The exosomes derived from these cells have shown promising results in numerous cell and animal experiments.
Unlike cell-based therapies, exosomes offer a cell-free approach that may provide similar regenerative benefits with improved safety profiles.
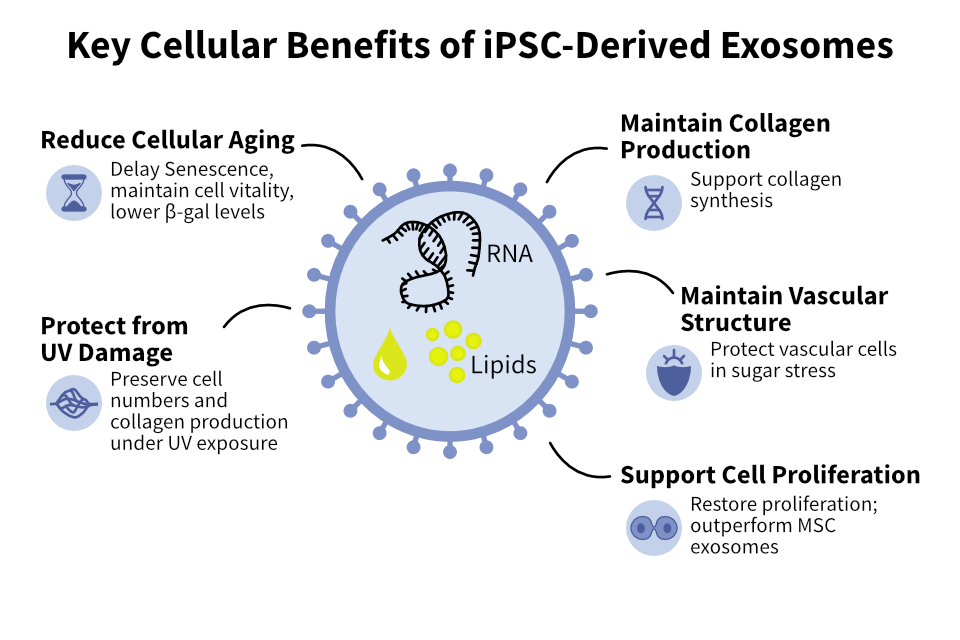
Key Cellular Benefits
Research has demonstrated multiple beneficial effects of iPSC-derived exosomes on cellular health.
Reduce Cellular Aging
Delay senescence, maintain cell vitality, and lower β-galactosidase levels associated with aging.
Protect from UV Damage
Preserve cell numbers and collagen production under UV exposure stress.
Maintain Collagen Production
Support ongoing collagen synthesis essential for tissue structure and skin health.
Maintain Vascular Structure
Protect vascular cells under sugar stress, supporting cardiovascular health.
Support Cell Proliferation
Restore cellular proliferation rates, outperforming MSC-derived exosomes in studies.
Enhanced Regeneration
Promote tissue repair and regeneration through targeted molecular signaling.
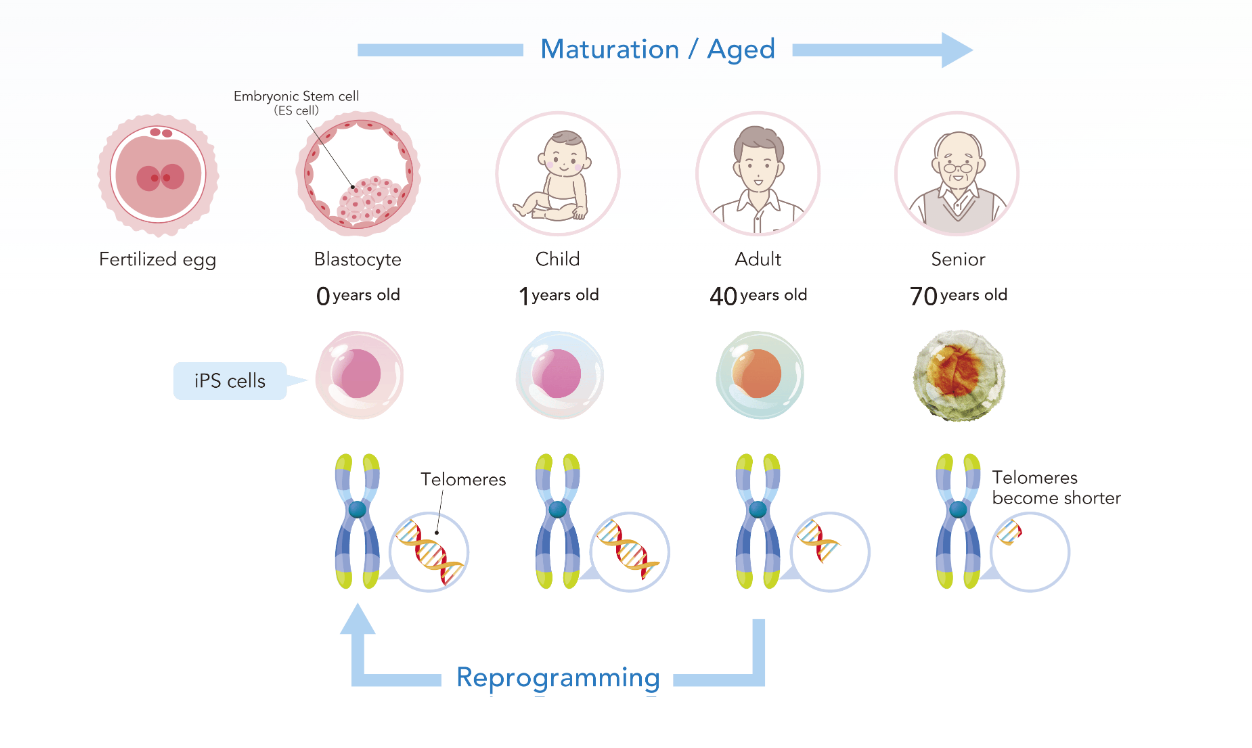
Why iPS-Derived?
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) are adult cells reprogrammed back to an embryonic-like state. This process restores youthful cellular characteristics, including telomere length.
As we age, our telomeres shorten, contributing to cellular aging and reduced regenerative capacity. iPS cells essentially "reset" this aging clock.
Virus-Free iPS Cells
Typically, iPS cells are generated by introducing reprogramming factors into somatic cells using gene introduction methods or viral methods. These methods carry the risk of genetic recombination.
Our iPS cells are established using a next-generation method utilizing mRNA, which eliminates the risk of genetic recombination or residual viruses.
mRNA Method: Because mRNA does not persist in the cells, it will not contaminate the culture supernatant or mix into the exosomes.
Traditional vs mRNA Method
Viral Methods
Risk of genetic recombination
Gene Introduction
Potential contamination
mRNA Method
No genetic risk, no contamination
Quality & Compliance
Our exosomes meet the strict regulatory standards of Japan, the US, and Europe.
GMP-Compliant Facility
The facilities are established for the manufacturing of cell products for regenerative medicine, with strictly defined standards for cleanliness, management methods, and manufacturing procedures.
- Monitoring airborne particulates and bacteria
- Frequent cleaning and periodic inspections
- Only trained personnel perform the work
Multi-Step Purification
Our iPS Exosomes are purified multiple times to remove components other than exosomes, such as those originally contained in the culture medium and cell waste products.
- Strict donor screening protocols
- Multiple tests at different time points
- High-concentration final product
Product Specifications
Available in two formats to meet different research and clinical needs.
Learn More About Our Research
Explore our published research or contact us for collaboration opportunities.


